Asgard Archaea unveil insights into complex cell origins
An international team of SciLifeLab affiliated researchers is making strides in unraveling the origins of complex eukaryotic cells by investigating Asgard archaea. These microorganisms, closely related to eukaryotes, offer valuable clues about the process of eukaryogenesis.
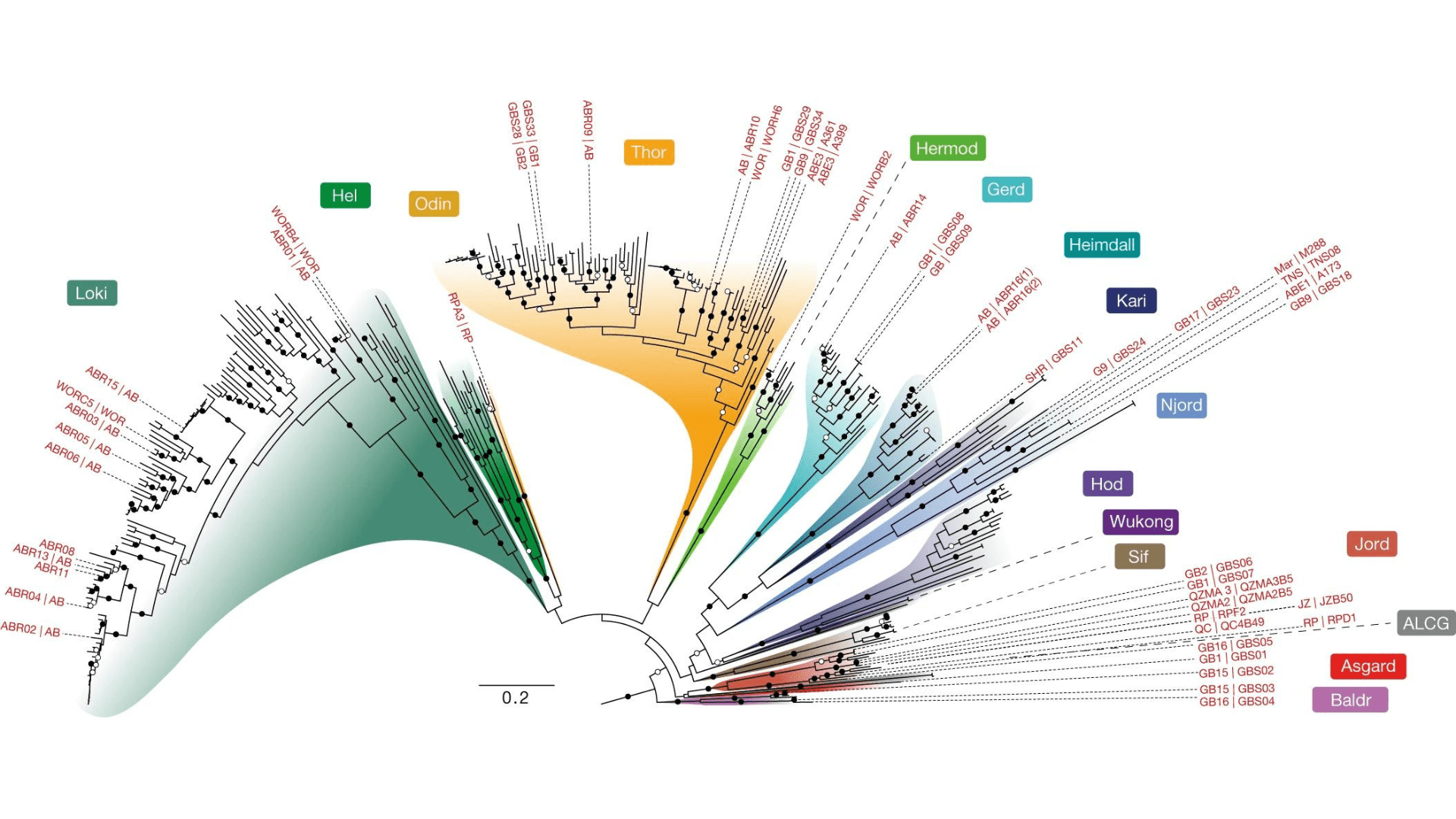
In a recent SciLifeLab-supported study published in Nature, researchers analyzed the genomic data of Asgard archaea to shed light on their evolutionary history. They discovered that eukaryotes form a nested clade within Asgard archaea, confirming a shared ancestry. The study also identified Hodarchaeales, a newly proposed order within Heimdallarchaeia, as the sister lineage to eukaryotes, refining our understanding of their relationship.
Examining genome evolution, the international team of researchers led by Microbial Single Cell Genomics co-founder Thijs Ettema also found intriguing parallels between Asgard archaea and eukaryotes. Both experienced significant gene duplication events, suggesting similar patterns of genome evolution. Notably, Asgard archaea underwent fewer gene loss events compared to other archaea, indicating unique genetic characteristics.
The study also offered insights into the environmental conditions of the last common ancestor of Asgard archaea. The scientists hypothesize that this ancestor was a thermophilic chemolithotroph, thriving in high-temperature environments and deriving energy from inorganic compounds. In contrast, the lineage leading to eukaryotes adapted to moderate temperatures, acquiring genetic traits for a heterotrophic lifestyle reliant on organic compounds. These findings contribute to our understanding of the prokaryote-to-eukaryote transition and the emergence of cellular complexity.
This research marks a significant step toward unraveling the mysteries of eukaryogenesis, shedding light on the remarkable journey from simple to complex life forms. As researchers continue to build upon these findings, Asgard archaea play a crucial role in uncovering the origins of complex cells.