A technique for detecting drug binding during drug development and in the clinic
SciLifeLab researchers from Uppsala University have demonstrated a new approach that enables highly precise visualization of the binding of drugs directly in patient tissues. The assay can help select compounds with specificity for particular target proteins, and it may inform selection of optimal therapy for individual patients.
Drugs are designed to bind their target proteins to influence biological functions for therapeutic purposes. Information about target engagement is therefore critical in drug discovery as well as in clinical routine. The new target engagement-mediated amplification (TEMA) technology uses DNA-conjugated drug molecules to visualize binding of the drugs to their targets.
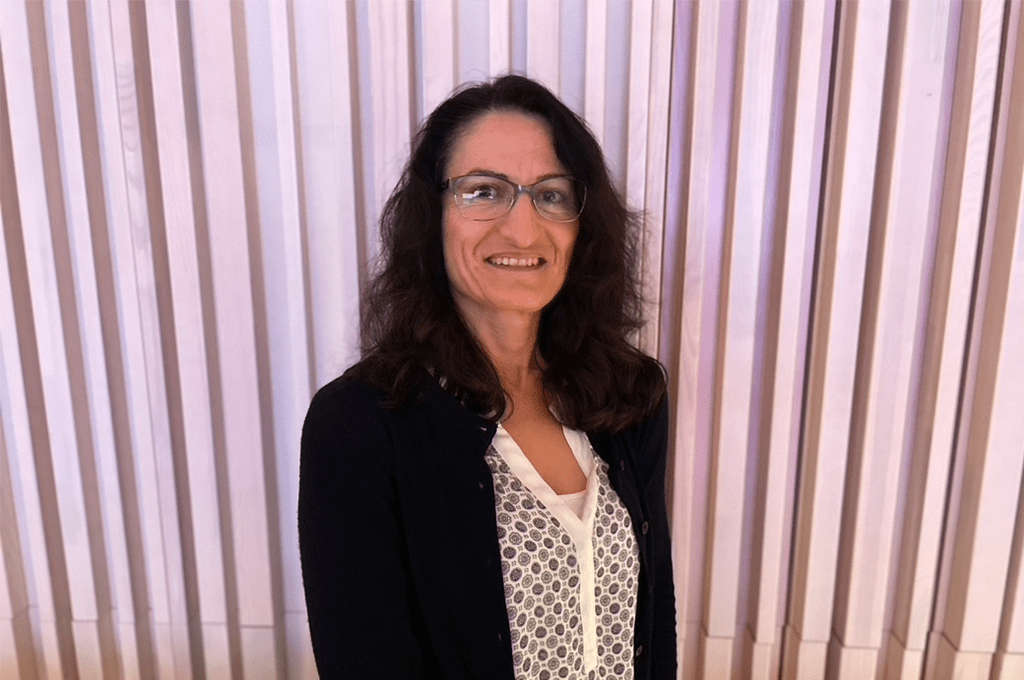
“TEMA represents a new promising approach to demonstrate target engagement by drugs in patient material, suitable for application in the drug discovery process and with a potential for predicting patient responses to drugs,” says Dr. Rasel A. Al-Amin, who is the first authors of the paper.
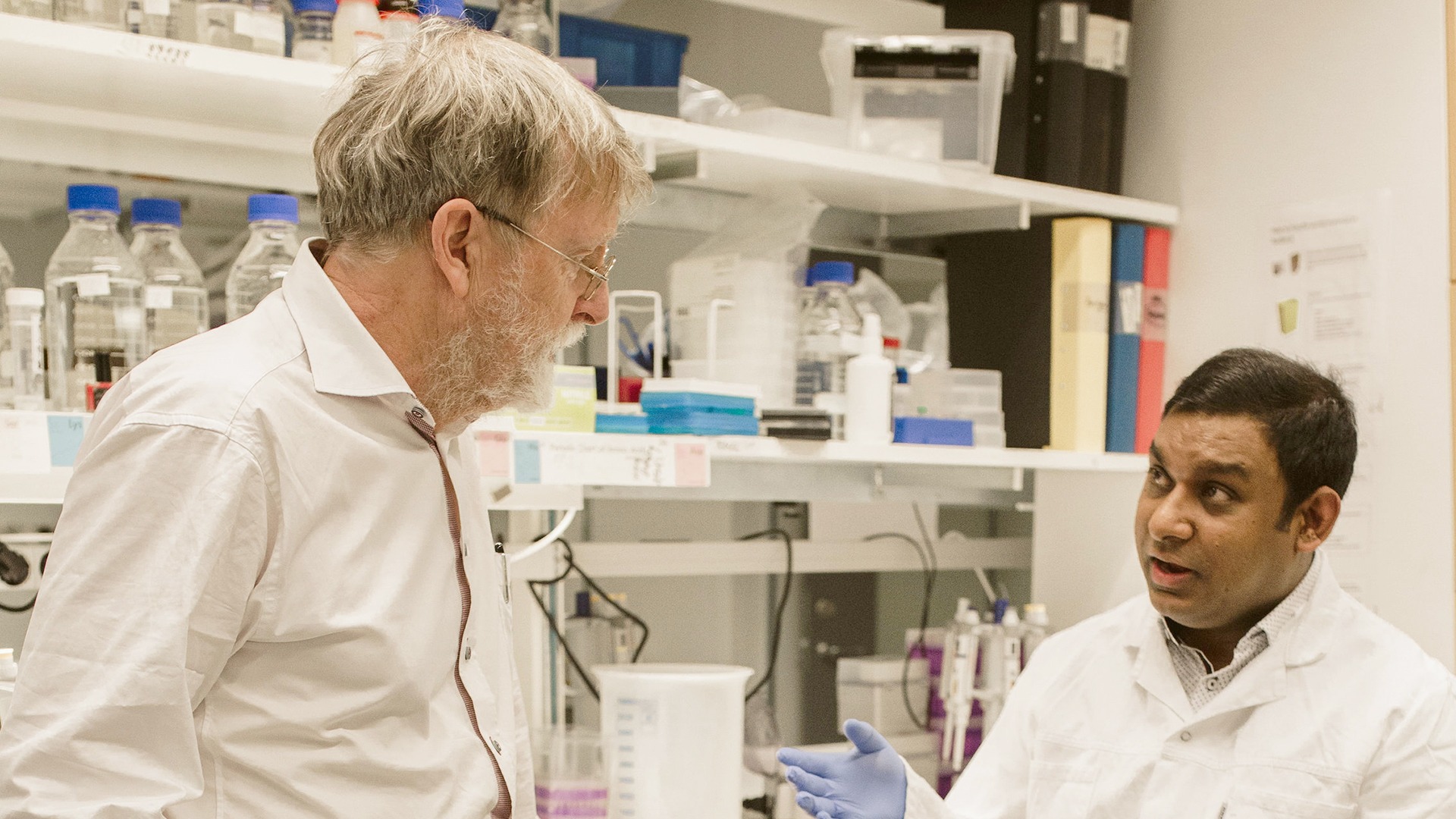
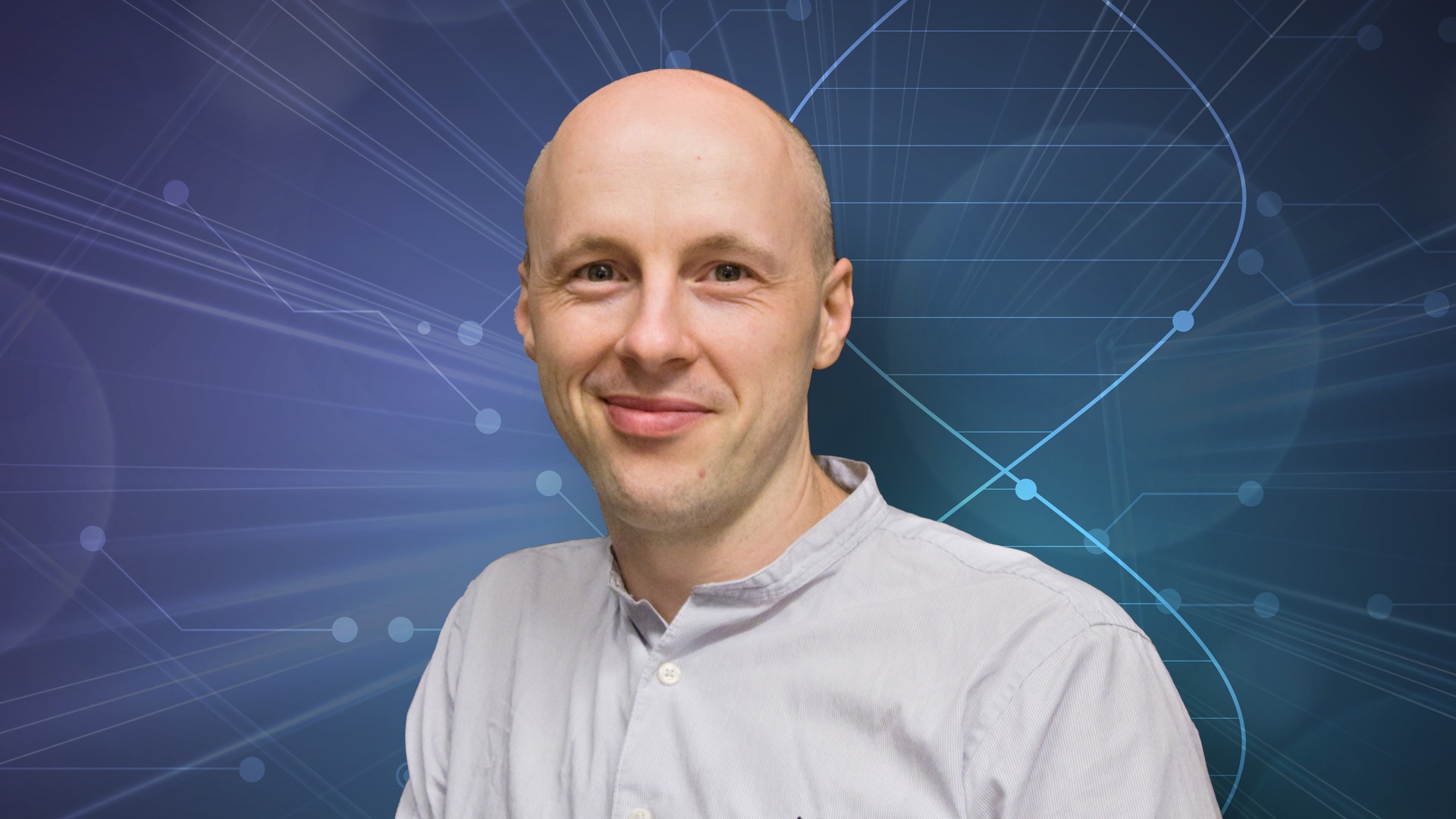
“The promising TEMA method can be used to analyze biopsy material from tumor patients in order to select optimal therapy or to evaluate the emergence of resistance mutations.” says SciLifeLab researcher Ulf Landegren, Professor of Molecular Medicine at Uppsala University, who is one of the senior authors of the study.
The TEMA method was developed mainly by Rasel Al-Amin with the help of coworkers in Ulf Landegren’s group at Uppsala University. The work was a collaboration with researchers at the Chemical Biology Consortium Sweden, Science for Life Laboratory, Department of Medicine (Solna), Karolinska Institute, Department of Chemistry BMC, Department of Medical Sciences, Department of Pharmacy, Uppsala University Drug Optimization and Pharmaceutical Profiling, Uppsala University and Medical University of Innsbruck.