Activation mechanism of the HCN ion channel revealed
Researchers from SciLifeLab have revealed the activation mechanism of the HCN ion channel by computer simulations, which was also later confirmed in the lab. HCN belongs to an important class of ion channels involved in heartbeat regulation and plays a crucial role in neurons.
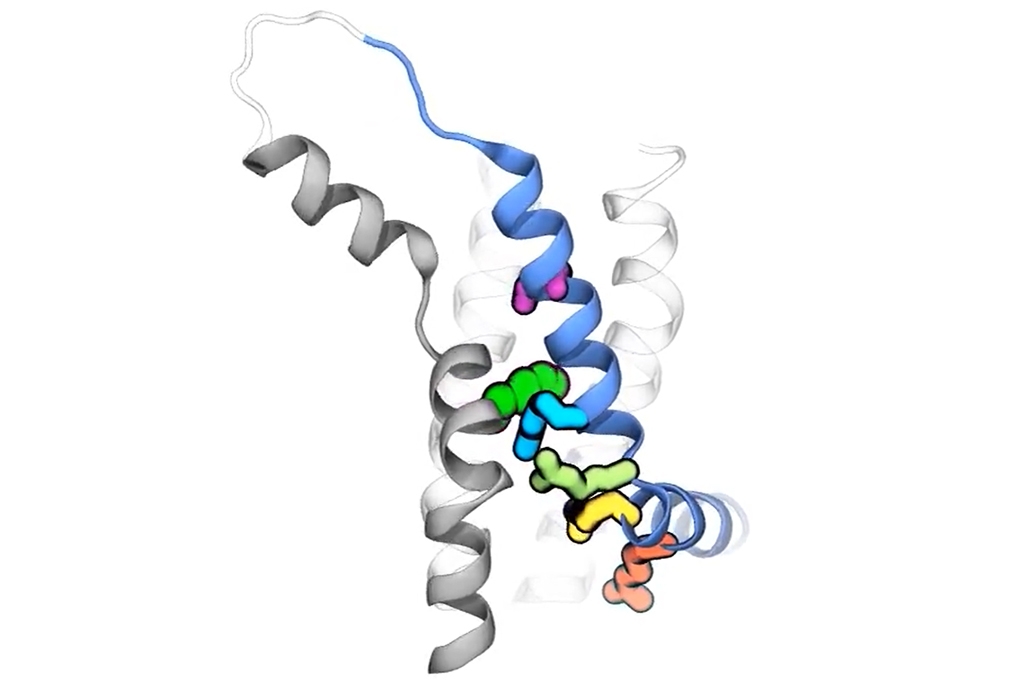
Most voltage-gated ion channels are opened by depolarization – which is when the cell membrane potential shifts from negative to positive. HCN ion channels however, are activated by hyperpolarization instead. The HCN voltage sensitive element is called S4 but so far, the mechanism of how it is involved in the activation of the channel is unknown.
“Most electrical signals in your brain are triggered by positive charges entering the cell, but HCN channels are special, as they work in the opposite way, triggered by positive charges exiting the cell. This means they have to work in a totally different way, that we couldn’t have predicted based on ‘standard’ models available so far” says last author Lucie Delemotte (SciLifeLab/KTH).
In a recent study, co-led by SciLifeLab Fellow Lucie Delemotte, researchers identified this novel mechanism by computer simulations which was later confirmed by wet-lab experiments led by Baron Chanda (University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA).
The S4 voltage sensor contains charged amino acids that responds to the electrical stimulus making it change position and subsequently break apart, dividing it into sub-helices which then can drive the channel gate open. This occurs while the rest of the channel architecture remains relatively unaltered and is crucial for the channel to open
The results, published in eLife, provide important information on how this type of ion channels work which in the future could make it possible to modulate their function. The study also demonstrates the power of computer simulations which potentially could cut down research time by years.