Services provided by our national research infrastructure
At SciLifeLab, we provide access to a range of pioneering technologies in molecular biosciences. Together, our capabilities enable the scientific endeavours of users from academia, industry and health care. Dedicated staff scientists can offer support throughout the experimental process – from study design to data handling.
Regardless of your particular field of work, you are welcome to seek support from units at SciLifeLab. Most of our technologies are agnostic to applications, meaning they can be used to address questions in a range of life science disciplines, e.g. precision medicine, ecosystem surveillance and evolutionary biology.
Questions? Contact info@scilifelab.se

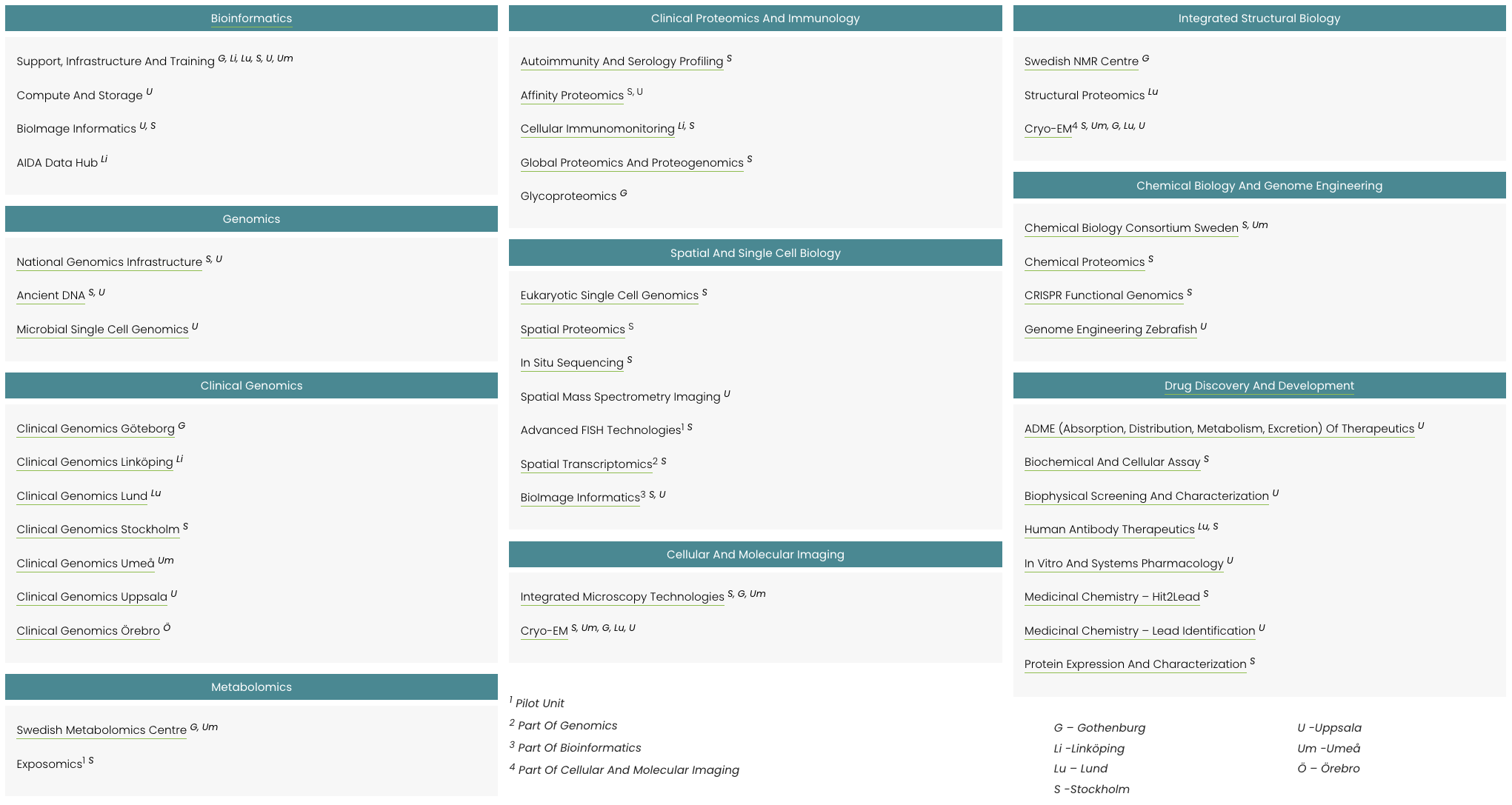
Explore our infrastructure
Select relevant technologies or platforms to navigate to relevant infrastructure services or technologies.
Recent user publications
The publications in this database are the result of research conducted at the units of SciLifeLab – both in user projects and technology development.
Incontinentia pigmenti underlies thymic dysplasia, autoantibodies to type I IFNs, and viral diseases.
J. Rosain, T. Le Voyer, X. Liu, (…), N. Landegren, MS. Anderson, JL. Casanova,
J. Exp. Med.221 (11)
The single-cell transcriptomic atlas iPain identifies senescence of nociceptors as a therapeutical target for chronic pain treatment.
P. Techameena, X. Feng, K. Zhang, S. Hadjab,
Nat Commun15 (1) 8585
IL-7-dependent and -independent lineages of IL-7R-dependent human T cells.
CA. Arango-Franco, M. Ogishi, S. Unger, (…), K. Warnatz, JL. Casanova, A. Puel,
J. Clin. Invest.134 (19)
Sex estimation using long bones in the largest burial site of the Copper Age: Linear discriminant analysis and random forest
S. Díaz-Navarro, S. Díez-Hermano, MA. Rojo-Guerra, (…), C. Valdiosera, T. Gunther, MH. Uriarte,
Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports58 104730
Merging multi-omics with proteome integral solubility alteration unveils antibiotic mode of action.
R. Maity, X. Zhang, FR. Liberati, (…), M. Gaetani, JA. Aínsa, J. Sancho,
Elife13
CDK4 is co-amplified with either TP53 promoter gene fusions or MDM2 through distinct mechanisms in osteosarcoma.
KH. Saba, V. Difilippo, E. Styring, (…), F. Haglund de Flon, D. Baumhoer, KH. Nord,
npj Genom. Med.9 (1) 42
By the numbers
Users across sectors
In 2023, SciLifeLab served about 1,800 unique users. 24% of the users were based in healthcare, industry and other governmental agencies. The remaining portion were based in academia.

Academic users
As SciLifeLab is a national infrastructure, the distribution of users is an important metric. In 2023, SciLifeLab served a total of 1,600 academic users – 61 % of which were based at institutions outside of SciLifeLab’s founding universities.

Infrastructure organization
Our national infrastructure is made up of ten technology platforms, each of which comprises a number of service units and are managed by appointed Platform Directors. For every unit, there is a Platform Scientific Director leading the scientific direction and a Head of Unit in charge of the daily operations.
Platform management
FAQ
Who can get support from SciLifeLab?
SciLifeLab is a national resource, open for researchers within academia, health care and industry from all over Sweden. International users are also welcome.
What does it cost to use technologies and expertise from SciLifeLab?
Swedish academic researchers using the platforms and units available at SciLifeLab typically pay for reagents, consumables, instrument time and part of labor related costs. Users from health care and companies are charged according to a full cost model. International academic users are also usually charged full cost, but are advised to contact the platform or unit directly to get information about the corresponding user fee policy.
How do you prioritize among projects?
The prioritization of service requests and project proposals differs between platforms and units, and is also dependent on the scope of the request. For standardized services, the “first-come first-served” principle is usually employed, while more comprehensive project proposals are prioritized based on feasibility analyses and judged degree of scientific impact. For large scale projects, platforms and units usually consult external prioritization bodies for the selection process. For more information, please contact the platform or unit directly.
What’s the waiting time for analysis and/or feedback?
Waiting times varies between platforms and unit, and is highly dependent on the current demand from users, as well as on the type and amount of analyses and services asked for. Please contact the platform or unit directly describing your request to get an estimate on the waiting time.